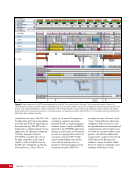
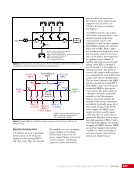
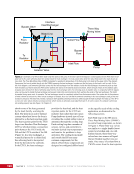
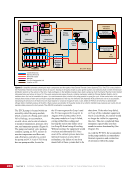
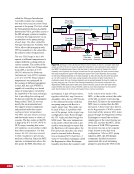
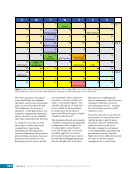
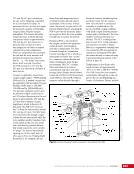
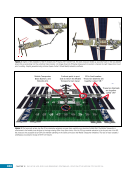
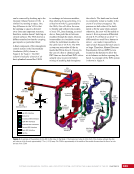
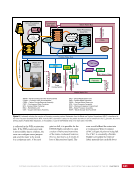
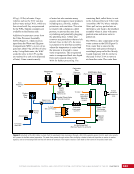
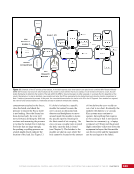
CHAPTER 7 SYSTEMS: MOTION CONTROL SYSTEM—NAVIGATOR OF THE HEAVENS 134 The terminal flight computer within the SM performs attitude control with thrusters when the Russian Segment is in attitude control, and responds to requests for desaturation thruster firings from the USOS GNC MDM when the US Segment is in attitude control. Control Modes The US Segment and Russian Segment flight software jointly works together through the use of several attitude control software modes. The software mode depends on what is operationally being done and which segment is in attitude control. The most common modes are listed below (see also Table 2): Table 2. US Segment/Russian Segment Control Mode Combinations Configuration US Mode Russian Mode Notes Usage Free Drift Free Drift Indicator or CMG/ Thruster Assist No active attitude control. Used immediately after docking while the docking interface is being made rigid. CMG/Thruster Assist CMG/Thruster Assist CMG/Thruster Assist US Segment controlling attitude with CMGs. Momentum management for quiescent operations, US control for vehicle grapples and capture. Thrusters Free Drift Thrusters Russian Segment Controlling with Thrusters. Large attitude maneuvers, Russian Vehicle dockings, reboosts. n Free Drift/Indicator—segment is not controlling attitude. n CMG/Thruster Assist—US Segment controlling attitude with CMGs, Russian Segment supporting with CMG desaturation firings when commanded from the US Segment. n Thrusters—Russian Segment controlling with thrusters. Typically, the configuration of the MCS will be CMG/Thruster Assist during routine orbit operations, with the US Segment in attitude control using a momentum management controller. The software is jointly reconfigured by both MCC-H and MCC-M to do a dynamic operation. The example in Table 3 illustrates the procedure for configuring from day-to-day momentum management to a configuration to support reboost. Times are referenced to time of reboost burn ignition, or time of ignition (TIG), in minutes. TIG is used as a countdown for reboost burns, which helps Mission Control personnel sequence out activities required to perform the burn. Table 3. ISS Reboost Timeline Time Center Action Notes TIG - 40 min MCC-H/MCC-M Uplink prep commands through Tracking Data Relay Satellite TIG - 30 min MCC-H Command handover to Russian Segment USOS Mode = Free Drift Russian Mode = Thrusters TIG - 25 min MCC-M Command reboost sequence to start TIG - 20 min Attitude maneuver to reboost attitude Under Russian Segment automatic software control TIG Reboost ignition Under Russian Segment automatic control TIG + 10 min MCC-M Maneuver back to normal stage TEA attitude TIG + 20 min MCC-H Command handover from Russian Segment USOS Mode = CMG/Thruster Assist Russian Segment Mode = CMG/Thruster Assist The US and Russian flight control teams jointly manage all of these operations by using a common set of flight procedures that are built
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: Scampersandbox (scampersandbox.tizrapublisher.com)