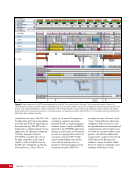
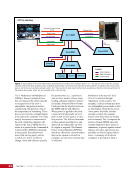
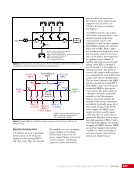
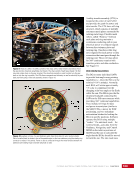
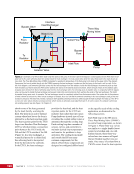
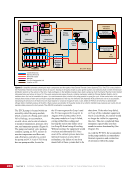
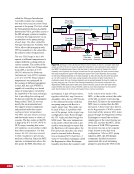
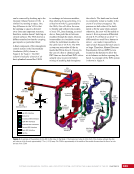
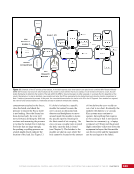
CHAPTER 8 DAY IN THE LIFE: DEBRIS AVOIDANCE—NAVIGATING THE OCCASIONALLY UNFRIENDLY SKIES OF LOW-EARTH ORBIT 144 locations. Figure 5 shows a map of sensors currently used to maintain the catalog of objects in orbit. SHY CLR MAU AMOS BLE JSpOC SOC CAV EGL DSC2-D MIT/LL GBII SBSS SAPH RTS DGC ASC THL COD FYL Figure 5. Current space SSN sensor locations. Sensors are labeled by the name of the complex in which they are housed, which is sometimes (but not always) geographic location. These sensors fall into four categories: 1) Phased Array Radars: Radar systems that rely on an electronically steered beam. n BLE – Beale Air Force Base, California n COD – Cape Cod Air Force Station, Massachusetts n CAV – Cavalier Air Force Station, North Dakota n CLR – Clear Air Force Station, Alaska n FYL – Fylingdales Royal Air Force Station, North York Moors. England n THL – Thule Air Force Base, Greenland n EGL – Eglin Air Force Base, Florida n SHY – Eareckson Air Station, Shemya Island, Alaska 2) Mechanical Radars: Radar systems that rely on a mechanically steered dish. n ASC – Ascension Royal Air Force Station, Ascension Island n GBII – Globus II radar station, Vardo, Norway n MIT/LL – MIT/Lincoln Labs, Massachusetts (includes Millstone and Haystack observatories) n RTS – Reagan Test Site, Marshall Islands 3) Ground-based Telescopes: n AMOS – Air Force Maui Optical and Supercomputing Site, Maui, Hawaii Installations of the Ground-based Electro-Optimal Deep Space Surveillance system: n SOC – Socorro, New Mexico n MAU – Maui, Hawaii n DGC – Diego Garcia Island 4) Space-based Optical: Sensors on satellites in Earth orbit. n SBSS – Space-based Space Surveillance, satellite system operated by the US Air Force n SAPH – Sapphire satellite system operated by the Canadian Armed Forces
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: Scampersandbox (scampersandbox.tizrapublisher.com)