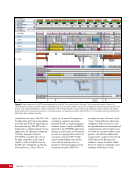
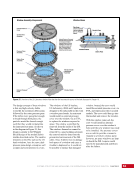
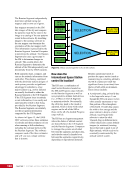
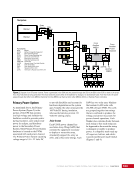
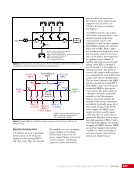
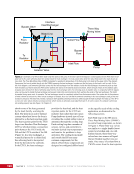
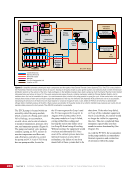
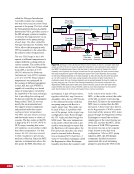
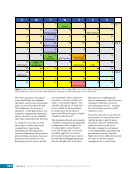
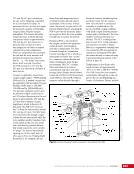
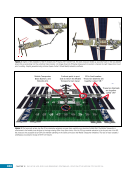
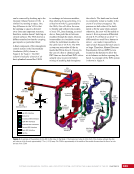
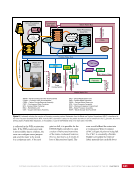
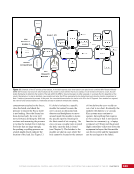
167 SYSTEMS: ELECTRICAL POWER SYSTEM—THE POWER BEHIND IT ALL CHAPTER 9 BCDU BGA SSU DCSU RBI 2 BCDU – Battery Charge/Discharge Unit BGA – Beta Gimbal Assembly DDCU – Direct-Current-to-Direct-Current Conversion Unit MBSU – Main Bus Switching Unit RBI – Remote Bus Isolator SSU – Sequential Shunt Unit MBSU RBI 1 RBI 6 RBI 5 RBI 3 RBI 4 BCDU BCDU DDCU Figure 6. DCSU distribution. Electricity comes in from the SSU through the BGA and, depending on the configuration of the RBI, is passed to BCDUs and downstream loads. Main Bus Switching Units The MBSUs are used to distribute primary power from the power channels to downstream DDCUs and other loads. They also provide the capability to cross-tie primary power channels to feed those DDCU loads in the event of a power channel failure or to restart a power channel. The S0 truss segment contains four MBSUs, each of which has input from two primary power channels and outputs to several DDCUs or USOS to RS power converters. See Figure 7. From MBSU 4 RBI 6 Power Supply DCSU – Direct Current Switching Unit MBSU – Main Bus Switching Unit RBI – Remote Bus Isolator RBI 9 Internal Cross-Tie DCSU 1A RBI 6 MBSU 4 RBI 7 RBI 7 RBI 14 MBSU 2 RBI 14 RBIs 2-5 to Loads RBIs 10-13 to Loads RBI 6 to MBSU 2 Power Supply RBI 1 RBI 8 DCSU 1B RBI 6 Figure 7. Example MBSU #1 distribution showing how power can flow using the RBIs to feed different DCSUs. The MBSUs provide a great deal of flexibility and redundancy in the electrical system by allowing various power sources to be connected, or tied, to other channels. Each MBSU contains two electrical buses and 14 RBIs. RBIs 1 and 8 are nominally the input power from primary power channels however, they can be used to backfeed power to a primary power channel, if needed, following a power channel failure. Other RBIs (2 through 5 and 10 through 13) are outputs to downstream loads. The ability to cross-tie the inputs to different buses is accomplished by closing RBIs that connect those power channel buses. The two buses internal to the MBSU can be cross-tied by closing RBI 9. Since RBIs 7 and 14 are connected to adjacent MBSUs, they can be cross-tied to other power channels. Although it would be technically possible to tie all downstream loads to one power channel, the channel would not have the power availability to actually power all of those loads. Similar to the DCSU power supply, the MBSU power supply has three possible inputs, which provides for a great deal of operational flexibility. Power can be provided upstream of RBIs 1 and 8, allowing either input power channel to supply an MBSU. Another MBSU can provide backup control power via RBI 6 to allow cross-tying as necessary if power was lost from both power channel inputs.
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: Scampersandbox (scampersandbox.tizrapublisher.com)