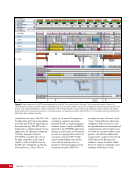
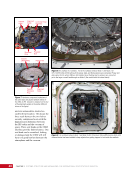
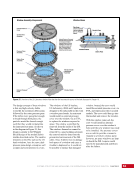
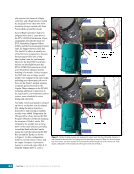
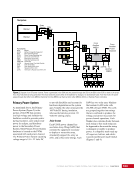
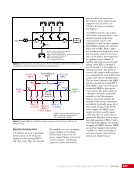
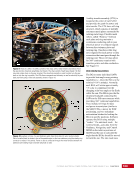
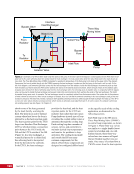
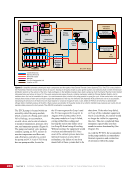
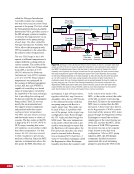
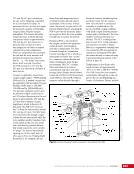
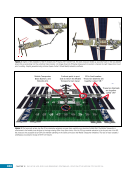
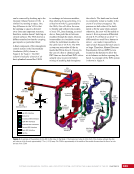
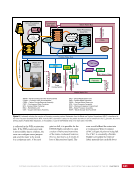
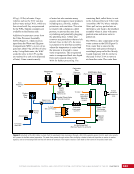
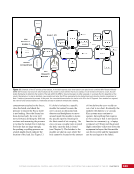
163 SYSTEMS: ELECTRICAL POWER SYSTEM—THE POWER BEHIND IT ALL CHAPTER 9 Primary Power System As mentioned above, the Primary Power System (Figure 2) is the portion of the EPS that operates at a high voltage and includes the hardware needed to generate power during insolation, store and provide power for eclipse, and distribute power to the Secondary Power System. Most Primary Power System hardware is located on the PVMs associated with each power channel. The Primary Power System operating voltage range is 155 ± 22 Volts DC to provide flexibility and account for hardware degradation as the system ages. Usually, the solar arrays provide 160 Volts DC during insolation, whereas the batteries provide 151 Volts DC during eclipse. SAW Array Strings SSU ECU DCSU RPCM BATT RPCM BGA Blanket Blanket Acronyms: BATT Battery BCDU Battery Charge/Discharge Unit BGA Beta Gimbal Assembly DCSU Direct Current Switching Unit DDCU DC to DC Converter Unit ECU Electronics Control Unit MBSU Main Bus Switching Unit PWR BUS Power Bus RPCM Remote Power Controller Module SAW Solar Array Wing SARJ Solar Alpha Rotary Joint SSU Sequential Shunt Unit [CHT] American to Russian Converter Unit SARJ [CHT]s To Another MBSU From Another MBSU From Another Power Channel MBSU RPCM PWR BUS Users RPCM DDCU DDCU DDCU BATT BCDU BATT BATT BCDU BATT BATT BCDU RPCM PWR BUS Users RPCM RPCM PWR BUS Users RPCM RPCM PWR BUS Users RPCM Users Users The System Figure 2. Diagram of an ISS power channel. Power is generated in the SAW and then passed through the SSU in the BGA to the DCSU or back to the arrays if too much electricity is being generated. The DCSU sends the power either to the batteries for storage or to downstream loads. From the DCSU, the power passes through the SARJ to the MBSUs. Electricity from the MBSUs can then be fed to other MBSUs, DDCUs, or Remote Power Controllers. Solar Arrays Each USOS power channel has one Solar Array Wing (SAW) that contains the equipment necessary to deploy or retract the array, structurally support the array on orbit, and collect solar energy. Each SAW has two solar array blankets that contain 16,400 solar cells (32,800 cells per SAW). The cells are grouped together into strings that are combined to produce the voltage and current necessary for power channel operations. Each blanket also contains diodes between each string so that each string can be bypassed in the event the string is damaged or unable to produce power. A collapsible mast made up of longerons, battens, and cables is positioned between each blanket (Figures 3 and 4).
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: Scampersandbox (scampersandbox.tizrapublisher.com)