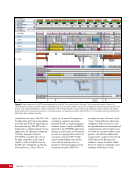
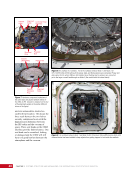
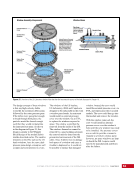
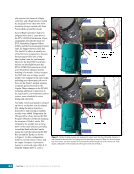
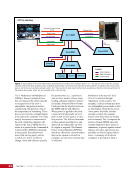
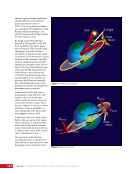
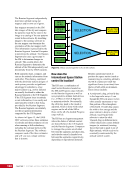
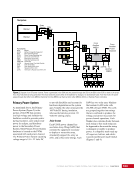
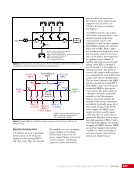
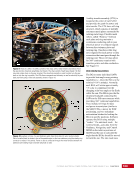
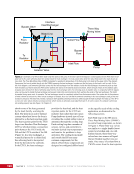
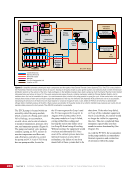
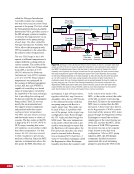
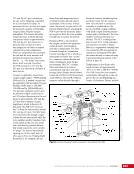
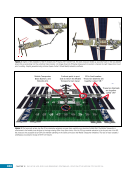
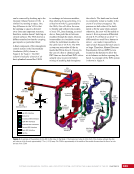
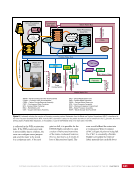
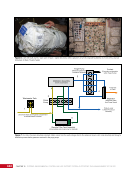
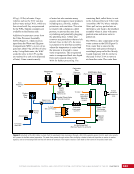
CHAPTER 9 SYSTEMS: ELECTRICAL POWER SYSTEM—THE POWER BEHIND IT ALL 164 Solar Array Blanket Blanket Box (lower half) Blanket Box (upper half) Guidewire Mechanisms Mast (partially extended, showing 2 bays) Mast Cannister (holds mast prior to deploy) 4.6 m (15.0 ft) 4.6 m (15.0 ft) 2.1 m (16.9 ft) Figure 3. Partially deployed solar array showing two bays extended (see also Figure 4). Upper Longeron Rigid Batten Frame Cable Diagonals Flexible Batten Corner Fitting Elbow Fitting Lower Longeron Figure 4. Solar array mast components. The longerons are collapsed when in the mast canister and then lock into place after extension. When retracted, each blanket folds into a box that is 51 cm (20 in.) tall. The mast is collapsed into a canister that is 2 m (6.6 ft) tall. When deployed, each SAW is 35 m (115 ft) long. A series of cables and a motor are used to deploy, retract, and hold a SAW taut. Each SAW was deployed during the ISS assembly Space Shuttle mission that delivered the associated PVM (Figure 5). Figure 5. Deployment of ISS solar arrays, showing the beginning of deployment with a couple of bays deployed (top), partially deployed with 16 bays (middle) and fully extended with all 32 bays extended (bottom). The P6 SAWs, channels 2B and 4B, were retracted during the ISS assembly sequence when it was necessary to move the P6 truss segment from its temporary location on top of the Z1 truss. The P6 SAWs were then redeployed during the STS-120/ISS-10A mission. The team experienced a lot of difficulties in getting the solar array blankets to retract and fold neatly into their boxes. Although this proved ultimately successful with the assistance of extravehicular activity (EVA) crew members, one of the channel 4B solar array blankets was damaged during the redeploy and required contingency EVA repair using unplanned/built-
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: Scampersandbox (scampersandbox.tizrapublisher.com)